Researchers find more evidence that antioxidants are key to preventing disease
11/15/2017 / By Russel Davis

A study published in the journal Nature Communications has revealed that the formation of cysteine hydropersulfides (CysSSH), a sulfur metabolite that is touted for its potent antioxidant properties, may be prompted by an enzyme found in the mitochondria. A team of international researchers from Japan, Hungary, the United Kingdom, and the United States has examined the pathway of CysSSH in order to carry out the study.
The findings have shown that the amino acid L-cysteine served as an initial building block for CysSSH synthesis, through a reaction facilitated by cysteinyl-tRNA synthetases (CARSs). According to the research team, CARS is a family of enzymes that can be found in mammalian cells. The researchers have explained that CARS enzymes are divided into two types, one of which can be seen in the cytoplasm of the cells and the other within its powerhouse or mitochondria.
A series of tests have also shown that the CARS enzymes in the mitochondria produce the majority of CysSSH and other persulfides. According to the experts, the enzymes work by traveling outside to the cell’s cytoplasm where it facilitates the reaction that produces the antioxidants. The scientists stress on a Science Daily entry that the dual roles of CARS enzymes provide a pathway within the cells that support sulfur respiration without requiring oxygen.
The results could lead to the development of new research on how enzymes could improve treatments for various disorders — such as diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease — by boosting antioxidant production, the researchers have stated.
Top 10 superfoods high in antioxidants
An article published on the Medium website has listed a number of superfoods that contain high levels of antioxidants. These include:
- Dark chocolate – Dark chocolate is notably rich in flavonoids and antioxidants.
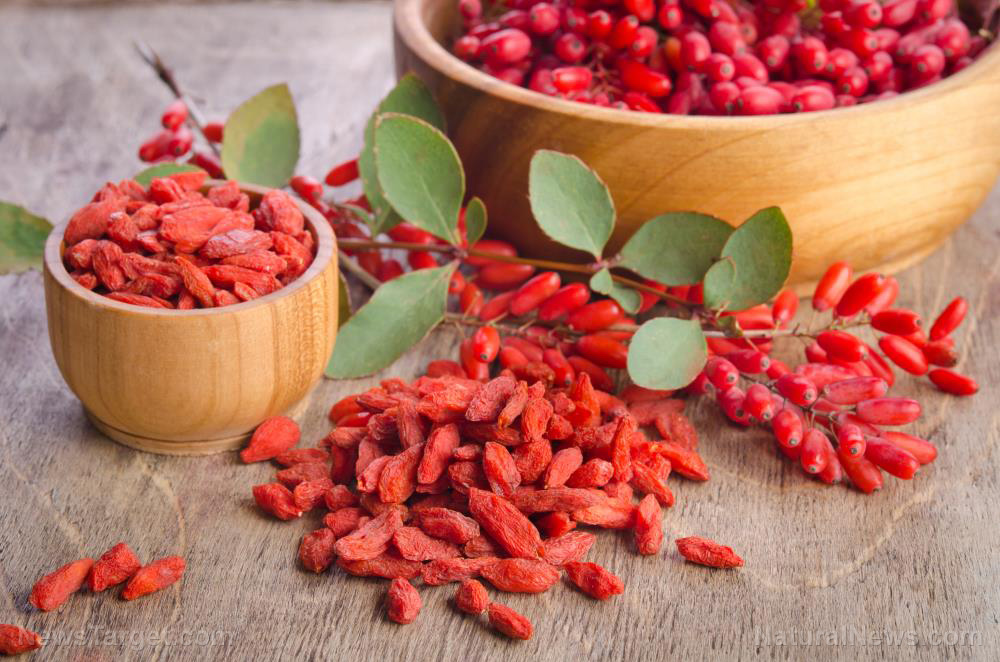
- Berries – Berries — such as blackberries, blueberries, strawberries, and cranberries as well as raspberries, goji berries, and elderberries — are excellent sources of potent antioxidants.
- Green leafy vegetables – Leafy greens such as spinach and kale are packed with phytochemicals that fend off inflammation and carcinogens.
- Green tea – The high antioxidant content in green tea is part of its charm. This is the same reason why it has been cultivated across the globe for centuries.
- Pomegranates, cherries, grapes, and raisins – The high antioxidant content in these fruits are also known to keep various diseases such as cancer and heart disease at bay.
- Nuts – Nuts are loaded with antioxidants called polyphenols. Tree nuts in particular — such as pecans, macadamias, cashews, and pistachios — are valued for their strong disease-fighting properties.
- Plums and prunes – Recent studies have shown that both plums and prunes are excellent sources of antioxidants.
- Herbs and spices – Spices like cloves, turmeric, and garlic as well as ginger and cinnamon are valued for their antioxidant content. The same can be said for herbs including oregano, basil, rosemary, and sage, a Live Strong article notes.
- Artichoke hearts – A significantly high amount of antioxidant can also be obtained from artichoke hearts.
- Kidney beans – Kidney beans are incredibly rich in disease-fighting compounds.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: antioxidants, disease treatment, fruits, healthy foods, vegetables