Chinese skullcap can prevent liver injury caused by heart failure
08/19/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
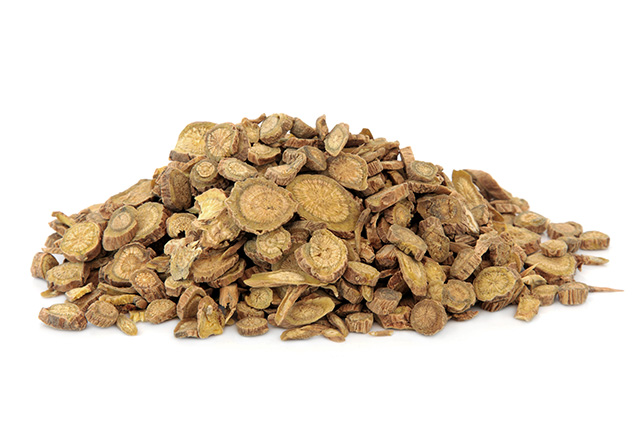

Scientists continue to explore the potential benefits of herbal remedies like Chinese skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis). The root of this plant contains a compound called baicalein, which is often used to treat liver disease in traditional Chinese medicine. In a recent study published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, baicalein was found to reduce liver injury induced by myocardial ischemia and reperfusion (I/R).
A team of researchers from the National Yang-Ming University School of Medicine in Taipei, Taiwan looked at the effects of baicalein from Chinese skullcap on liver damage caused by myocardial I/R. For their study, the researchers pretreated rats with three, 10, or 30 milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) baicalein 10 minutes before they induced myocardial I/R via 40-minute occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery and three-hour reperfusion.
The researchers found that pretreatment with baicalein significantly decreased aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) serum levels as well as apoptosis in the liver. It also decreased the levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-a), interleukin-1-beta (IL-1B), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). In addition, baicalein treatment increased B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and reduced Bax levels in the liver. Both Bcl-2 and Bax are proteins that regulate cell death. Baicalein also increased the phosphorylation of prosurvival kinases, including Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2).
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that baicalein can effectively reduce liver injury induced by myocardial I/R by regulating cell death in the liver. This study was published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
Baicalein from Chinese skullcap also attenuates liver damage caused by acetaminophen use
Pharmaceutical drugs like acetaminophen – a widely used antipyretic and analgesic drug – can cause side effects. One of the worst side effects of acetaminophen is liver damage.
A study published in the journal Molecules showed that baicalein from Chinese skullcap could reduce liver damage caused by acetaminophen. Baicalein possesses various pharmacological properties, such as anticancer, antioxidative, antivirus, and antibacterial.
In the study, researchers from Jilin Agricultural University in China investigated the effects of baicalein on acetaminophen-exposed mice with liver injuries. They also assessed the mechanism behind its liver-protective activity. (Related: Tylenol can kill you; new warning admits popular painkiller causes liver damage, death.)
They reported that pretreatment with baicalein significantly reduced IL-6, IL-1B and TNF-a levels in a dose-dependent manner. Baicalein also dose-dependently reduced hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration as well as the depletion of superoxide dismutase, glutathione, and catalase in the liver.
Pretreatment with baicalein substantially ameliorated acetaminophen-induced liver damage and histological hepatocyte changes. Baicalein also decreased acetaminophen-induced autophagy by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway — a signaling pathway important for the regulation of the cell cycle — and the expression of proteins involved in autophagy. Furthermore, the researchers found that the protective effect of baicalein against liver damage involves signaling pathways important for cell division, proliferation, and death.
The researchers concluded that baicalein can protect the liver from acetaminophen-induced liver damage and can be used to treat liver injuries.
Other ways to keep your liver healthy
Aside from taking health supplements, making these healthy lifestyle changes can help prevent liver disease:
- Avoid contaminated needles.
- Avoid direct contact with toxins, such as those from cleaning products, aerosol sprays, chemicals, additives, and pesticides.
- Avoid sharing items used for personal hygiene.
- Avoid using drugs.
- Exercise consistently.
- Follow a balanced diet.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
For more studies on baicalein and other natural medicines for liver damage, visit LiverDamage.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alanine transaminase, ALT, alternative medicine, alternative therapies, alternative treatment, apoptosis, aspartate transaminase, AST, baicalein, cardiac surgery, cardiovascular health, chinese skullcap, disease treatments, healing, heart disease, herbal medicine, Herbs, inflammation, liver damage, liver health, liver injury, myocardial ischemia and reperfusion, natural cures, natural medicine, natural treatment, prevention, remedies, research, TCM, therapies, traditional Chinese medicine
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 HEART NEWS